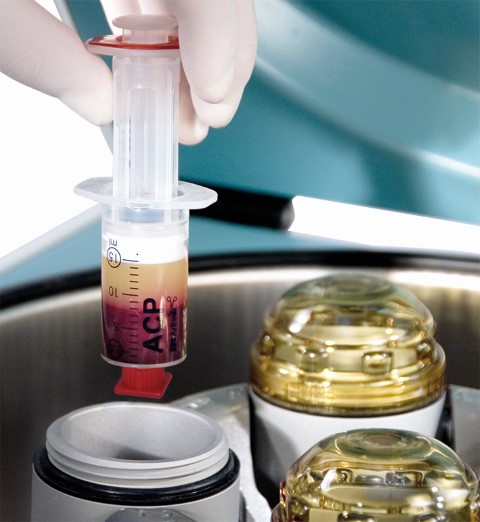
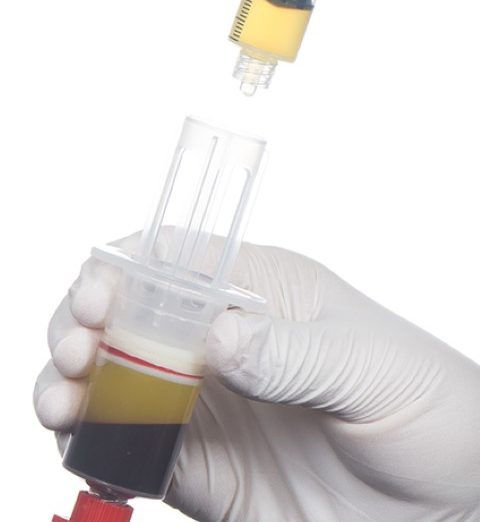
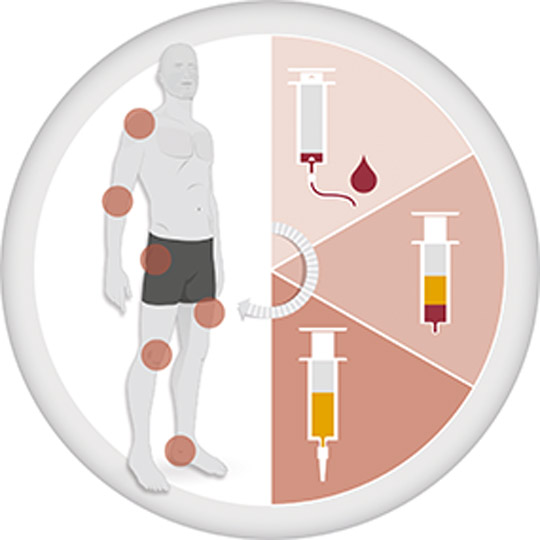
PRP (platelet rich plasma) therapy takes advantage of the knowledge that our blood contains healing agents and growth factors that can initiate and support healing processes in the case of injuries or chronic diseases. Several studies have shown that PRP has a high density of cytokines that reduce inflammation, postoperative blood loss, scarring, and infection, and on the other hand, promote healing of bones, wounds, and muscle and soft tissue injuries. Thus, PRP treatment in joints, tendons, ligaments and muscles is a procedure that we use regularly.
The background to the mode of operation is that platelets (thrombocytes) obtained from the blood degranulate after injection, releasing various growth factors and cytokines (signaling molecules) that have a regenerative capacity. In addition, in osteoarthritis, the toxic inflammatory effect on cartilage cells is inhibited and PRP also increases the synthetic activity of cartilage. PRP thus improves the joint environment and protects it from further degeneration.
Due to the long known positive effects of hyaluronic acid on cartilage, a combination of hyaluronic acid and PRP is the best possible option to heal the joint as international studies show. Depending on the region and damage, it may be necessary to apply 3-6 times, 7-14 days apart.